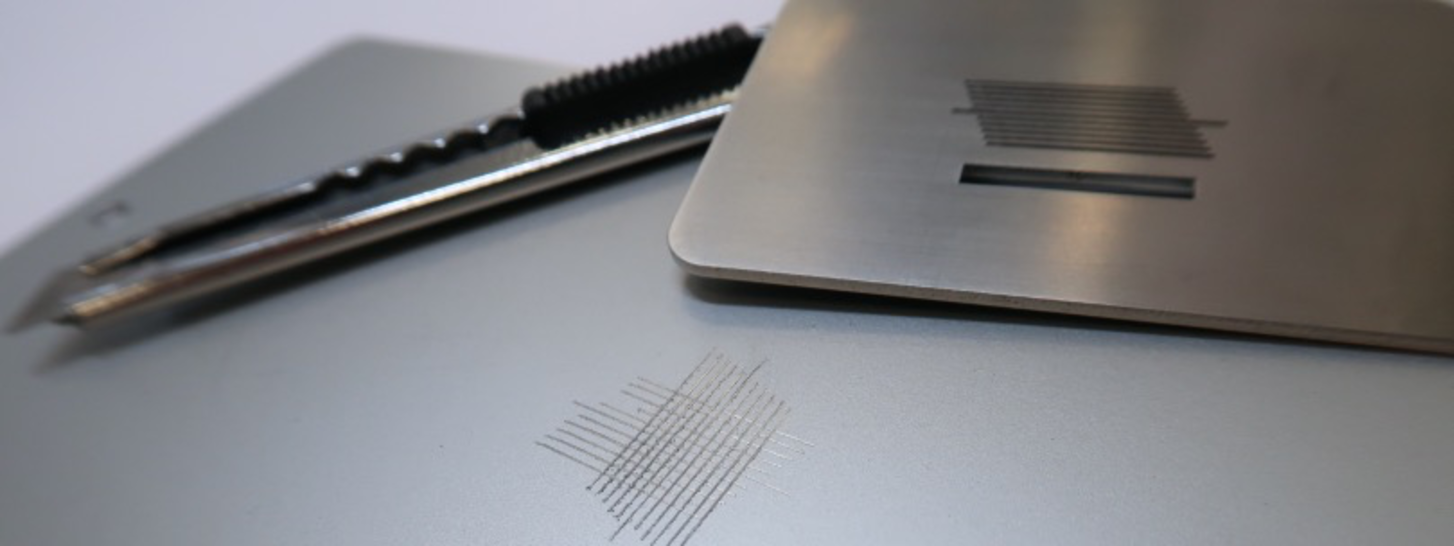
-
 Belgium nederlands
Belgium nederlands -
 Belgium français
Belgium français -
 Canada english
Canada english -
 Canada français
Canada français -
 China chinese
China chinese -
 Czech Republic čeština
Czech Republic čeština -
 Deutschland deutsch
Deutschland deutsch -
 France français
France français -
 Hungary magyar
Hungary magyar -
 International english
International english -
 Italy italiano
Italy italiano -
 Netherlands nederlands
Netherlands nederlands -
 Poland polski
Poland polski -
 Russia русский
Russia русский -
 Slovakia slovenčina
Slovakia slovenčina -
 Switzerland français
Switzerland français -
 Switzerland deutsch
Switzerland deutsch -
 Turkey Türkçe
Turkey Türkçe -
 USA english
USA english
